When choosing the right automation tool, n8n and Zapier are two popular options catering to different audiences and needs. While both allow you to automate tasks between apps, their approach, flexibility, and cost structures differ.
1. Ease of Use and Customization
Zapier
is known for its user-friendly, no-code interface, making it an ideal choice for non-technical users. You can create simple "Zaps" with just a few clicks by selecting triggers and actions across thousands of supported apps. However, this simplicity comes at the cost of flexibility. Advanced workflows involving conditions, loops, or custom scripts often hit limitations quickly.
n8n
offers a low-code environment with a visual editor that supports conditional logic, JavaScript functions, and data manipulation. While there's a slight learning curve, n8n provides far more control and customization, which is essential for developers and power users building complex automations.
2. Cost Comparison
Zapier operates on a freemium model, but becomes expensive as your needs grow. Its free plan is limited to 100 tasks/month, and advanced features like multi-step Zaps, filters, and custom logic are locked behind premium tiers.
n8n, however, is free and open-source, allowing users to self-host it without restrictions. This makes it a cost-effective choice, especially for startups and businesses with high-volume automation needs. For those preferring a hosted solution, n8n Cloud offers competitive pricing.
3. Flexibility and Scalability
n8n excels in flexibility and scalability. With support for over 350 integrations and the ability to create custom nodes, it can grow with your business. Its self-hosting capability also means you retain complete control over your data and infrastructure.
Zapier is great for simple automations, but n8n is better suited for users who need scalable, customizable workflows and more control over their automation processes.
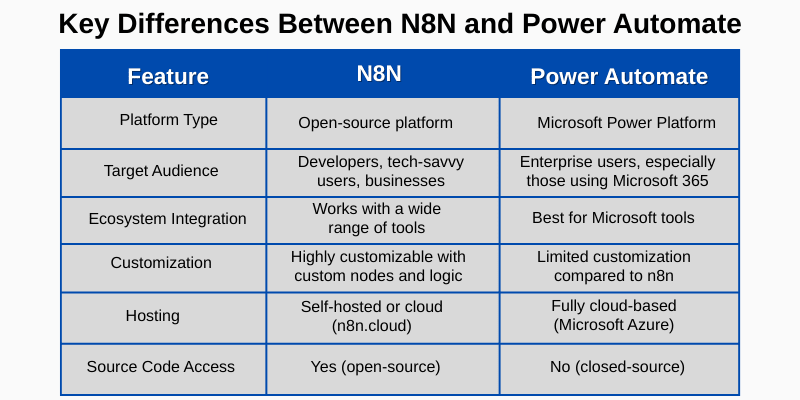
4. n8n vs Power Automate: Key Differences
Power Automate, part of the Microsoft Power Platform, is designed for enterprise users looking to automate workflows across Microsoft 365 and other Microsoft services. It shines in environments heavily invested in Microsoft tools like SharePoint, Outlook, Teams, and Dynamics 365.
n8n is an open-source automation platform built for flexibility and independence. It supports hundreds of integrations and can be extended with custom logic and nodes. You're not limited to a single ecosystem—n8n lets you integrate apps from Google, Airtable, OpenAI, Slack, and more.
5. Microsoft Integration vs Open-Source Approach
Power Automate offers tight, native integration with Microsoft tools and is ideal for organizations already using Microsoft infrastructure. However, it lacks the open customization capabilities that developers often require.
n8n's open-source model allows you to self-host it, modify the core, and fully control data flow, making it appealing to startups, developers, and privacy-conscious businesses.
6. Business Use Cases Comparison
- Power Automate is well-suited for automating internal business processes like document approvals, email flows, or SharePoint updates.
- n8n is more versatile for API-based automation, marketing workflows, AI integrations, and multi-platform data sync.
7. What is the Difference Between n8n and Airflow?
Apache Airflow is a powerful tool for orchestrating complex data pipelines, primarily in data engineering and analytics workflows. It's built for technical teams managing tasks with strict scheduling, retries, and dependency management.
8. Use Cases: Data Pipelines vs General Automation
- Airflow excels in batch-processing ETL jobs, big data, and analytics.
- n8n focuses on general-purpose workflow automation—from lead generation and API integrations to marketing and customer service automation.
9. Technical Complexity and Developer Focus
Airflow requires a solid understanding of Python, DAGs, and a backend setup. It's highly technical and best for data engineers.
While developer-friendly, n8n is much easier to get started with. It offers a drag-and-drop interface and low-code functionality, making it more accessible for broader use cases beyond data engineering.