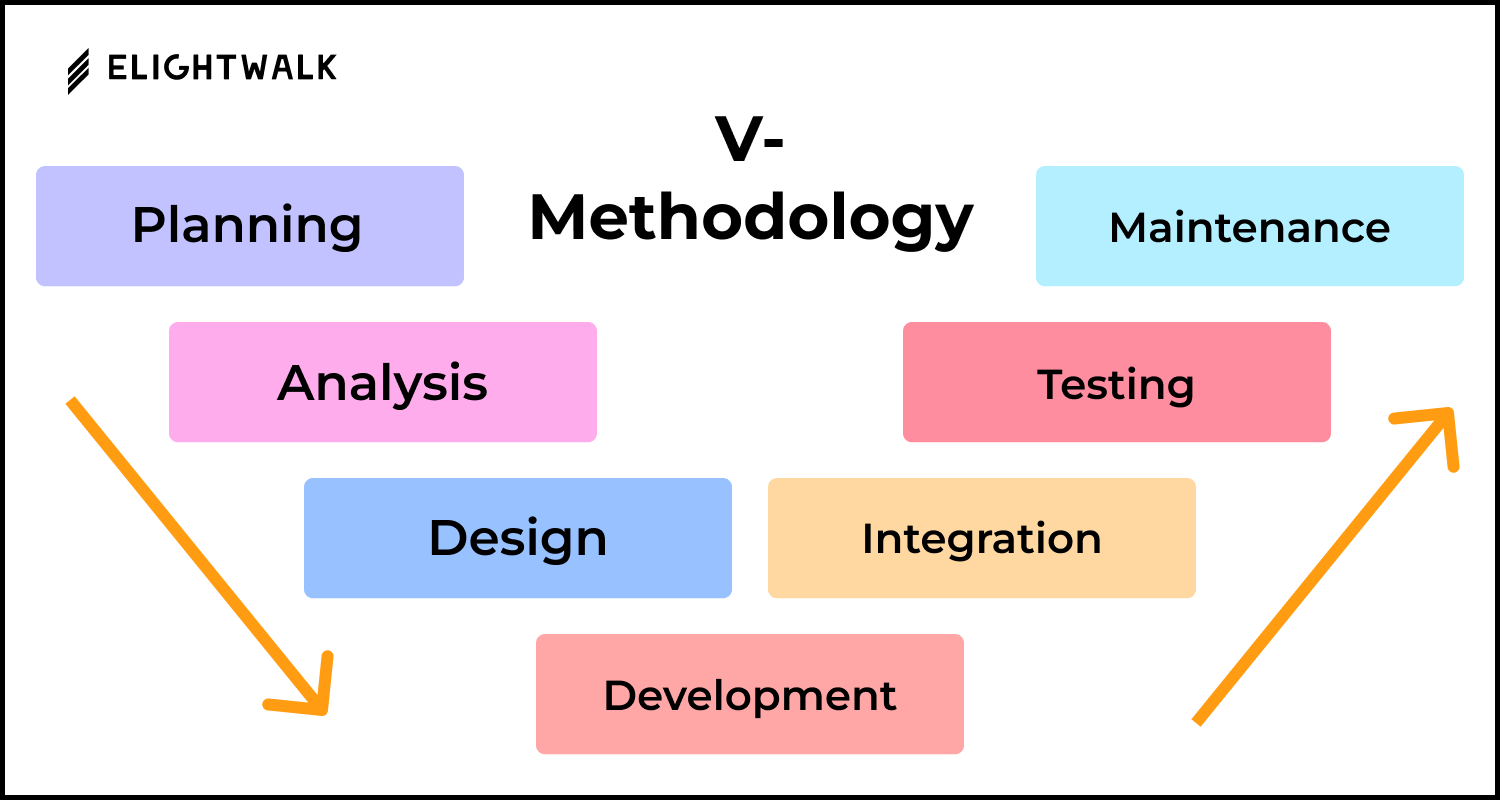
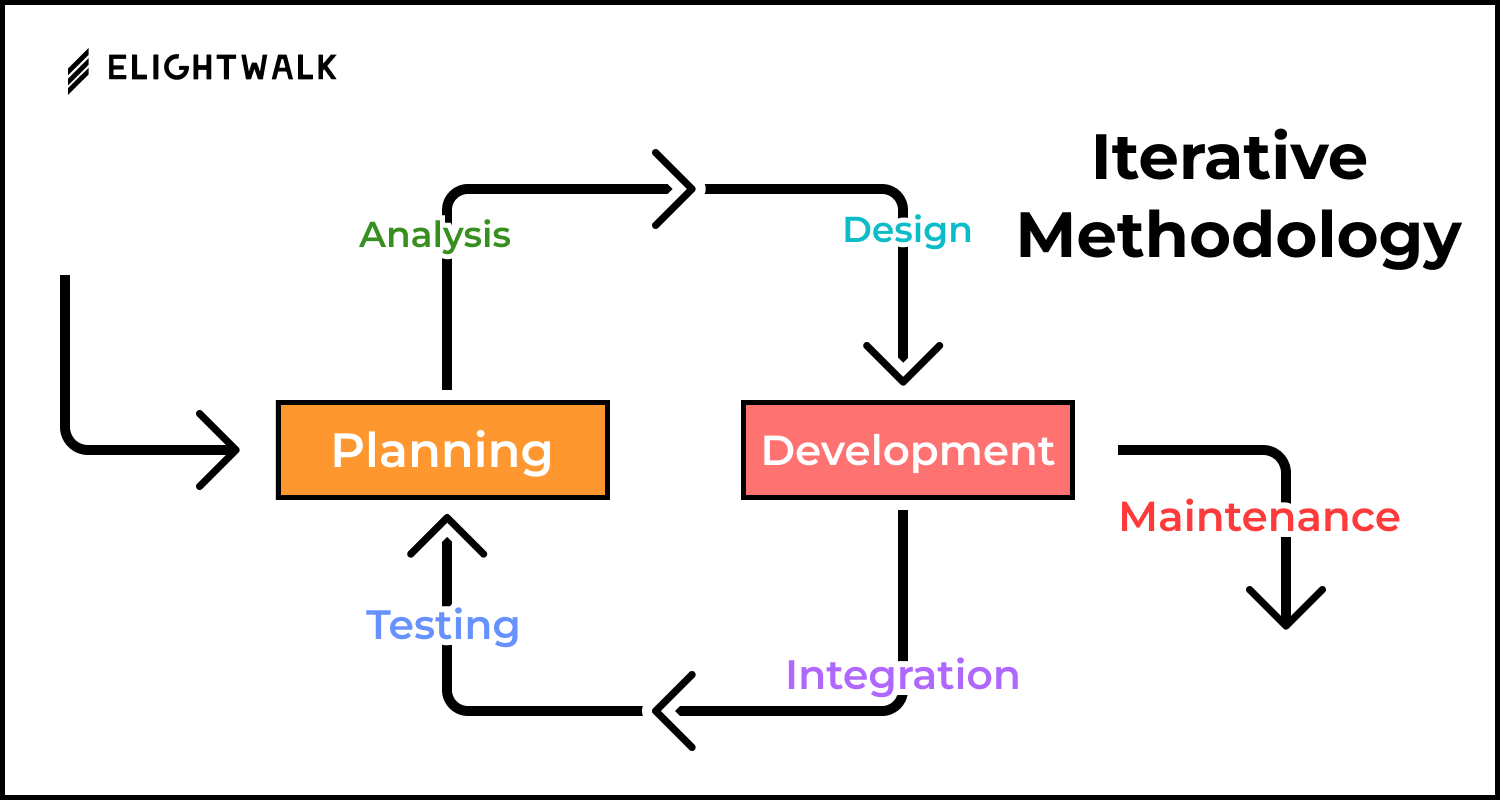
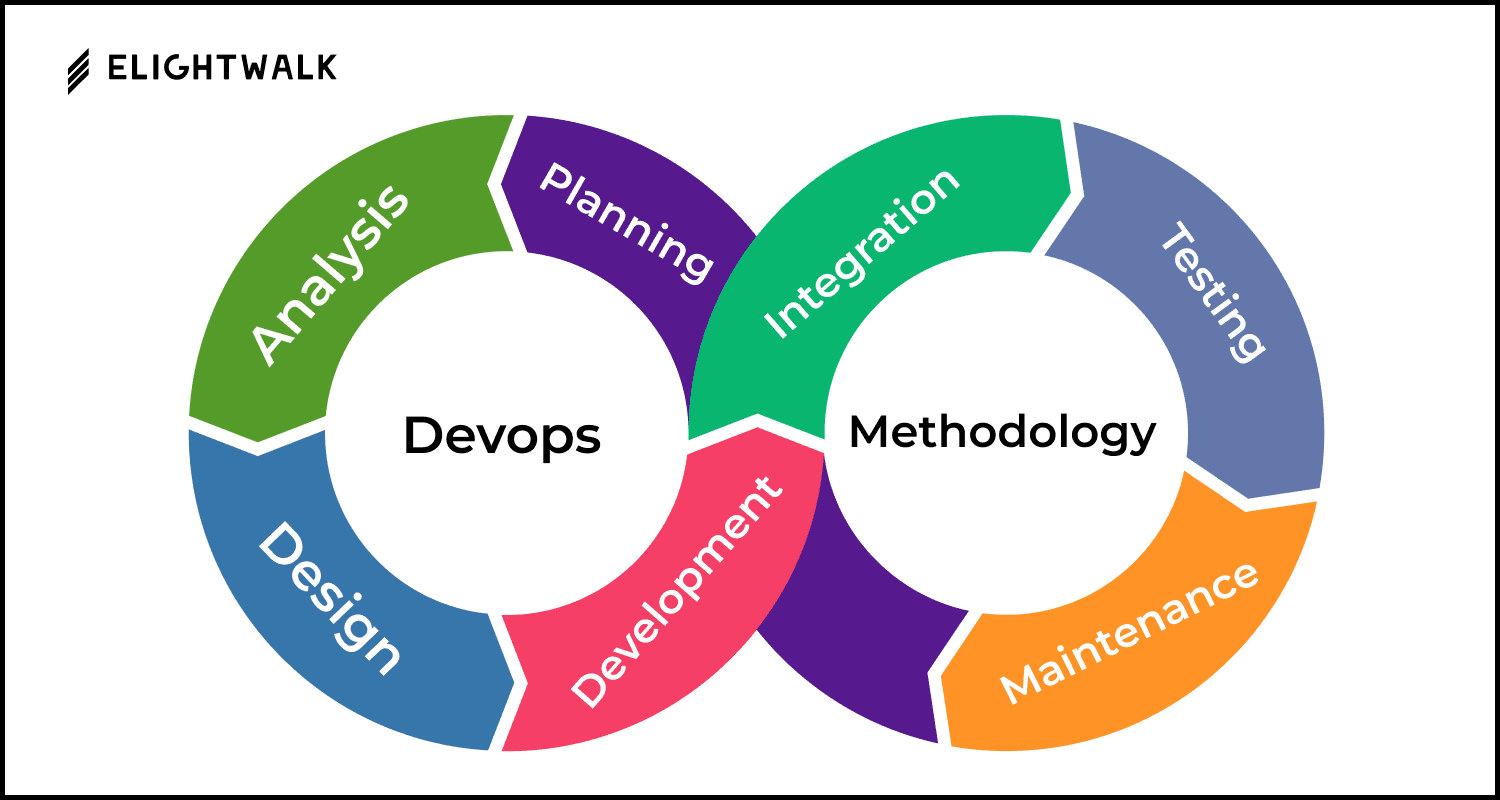
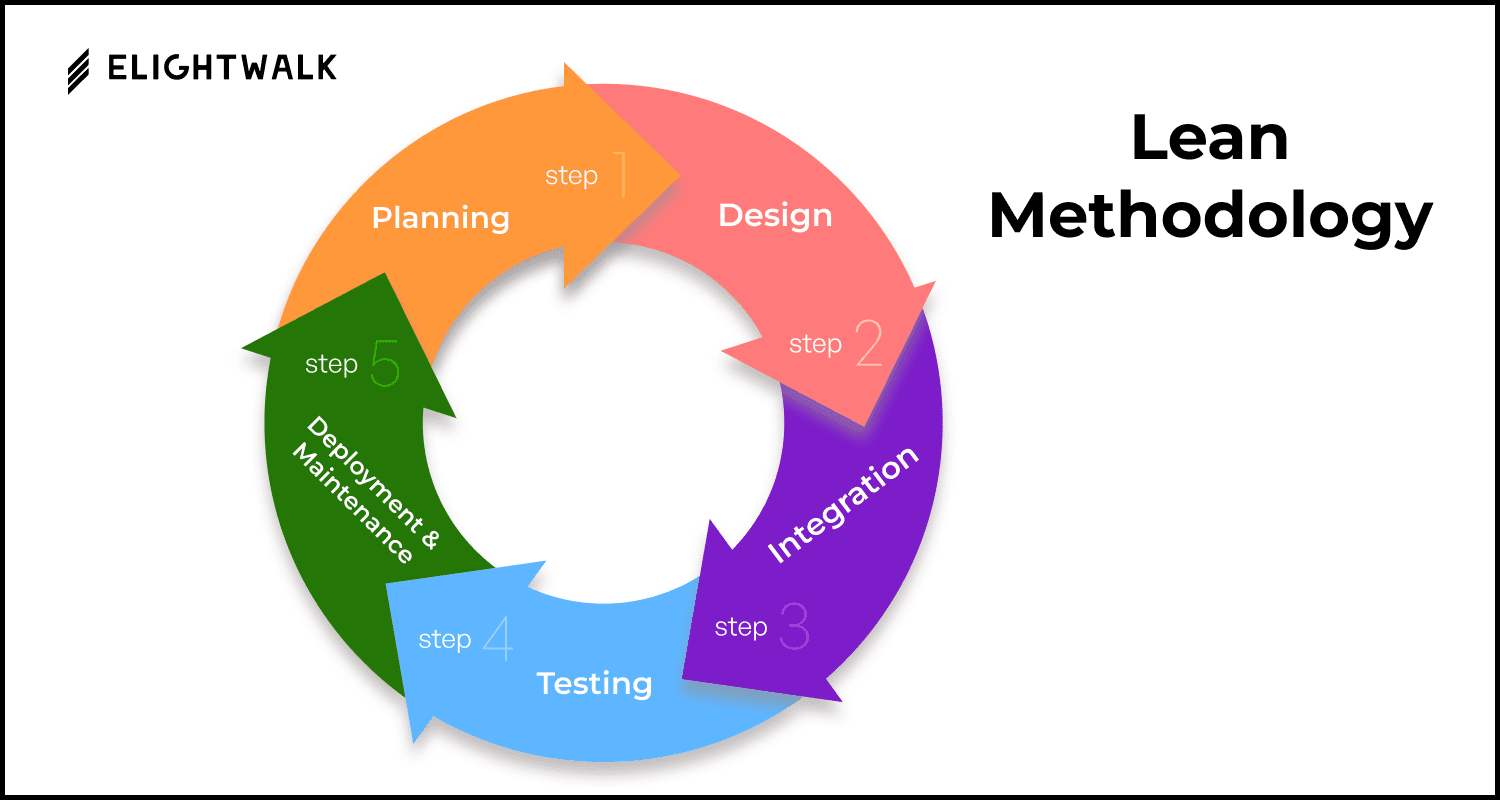
The System Development Life Cycle (SDLC) is a structured methodology used by software developers, engineers, and IT professionals to design, develop, test, and deploy software systems. Each phase of the SDLC plays a critical role in ensuring the software is high-quality, reliable, cost-effective, and aligned with stakeholder requirements.
- Planning and Feasibility Analysis
- Requirements Analysis
- System Design and Prototyping
- Software Development
- Testing and Quality Assurance (QA)
- Implementation and Integration
- Operations and Maintenance
Now, let’s take a closer look at each of these stages.
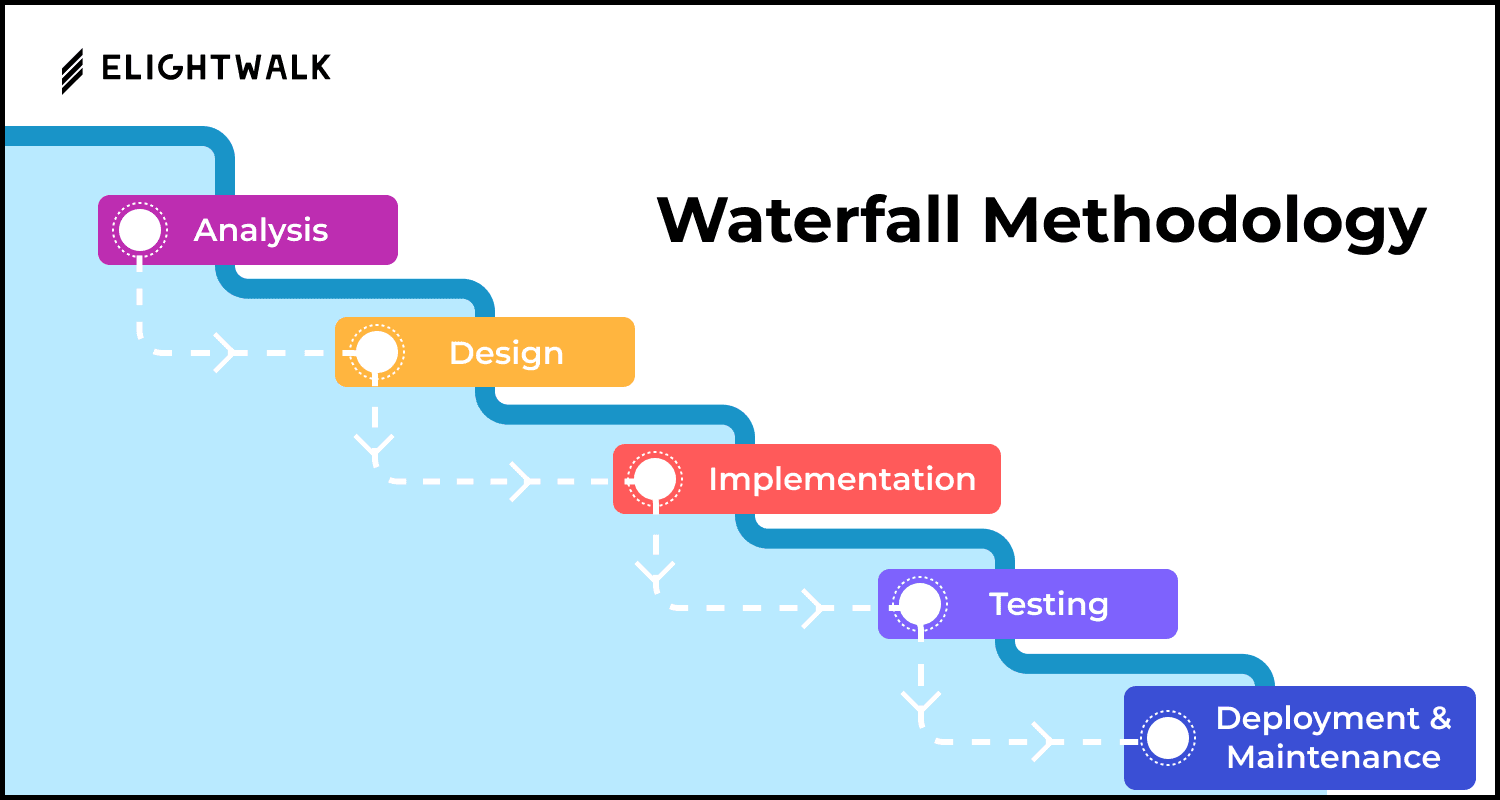
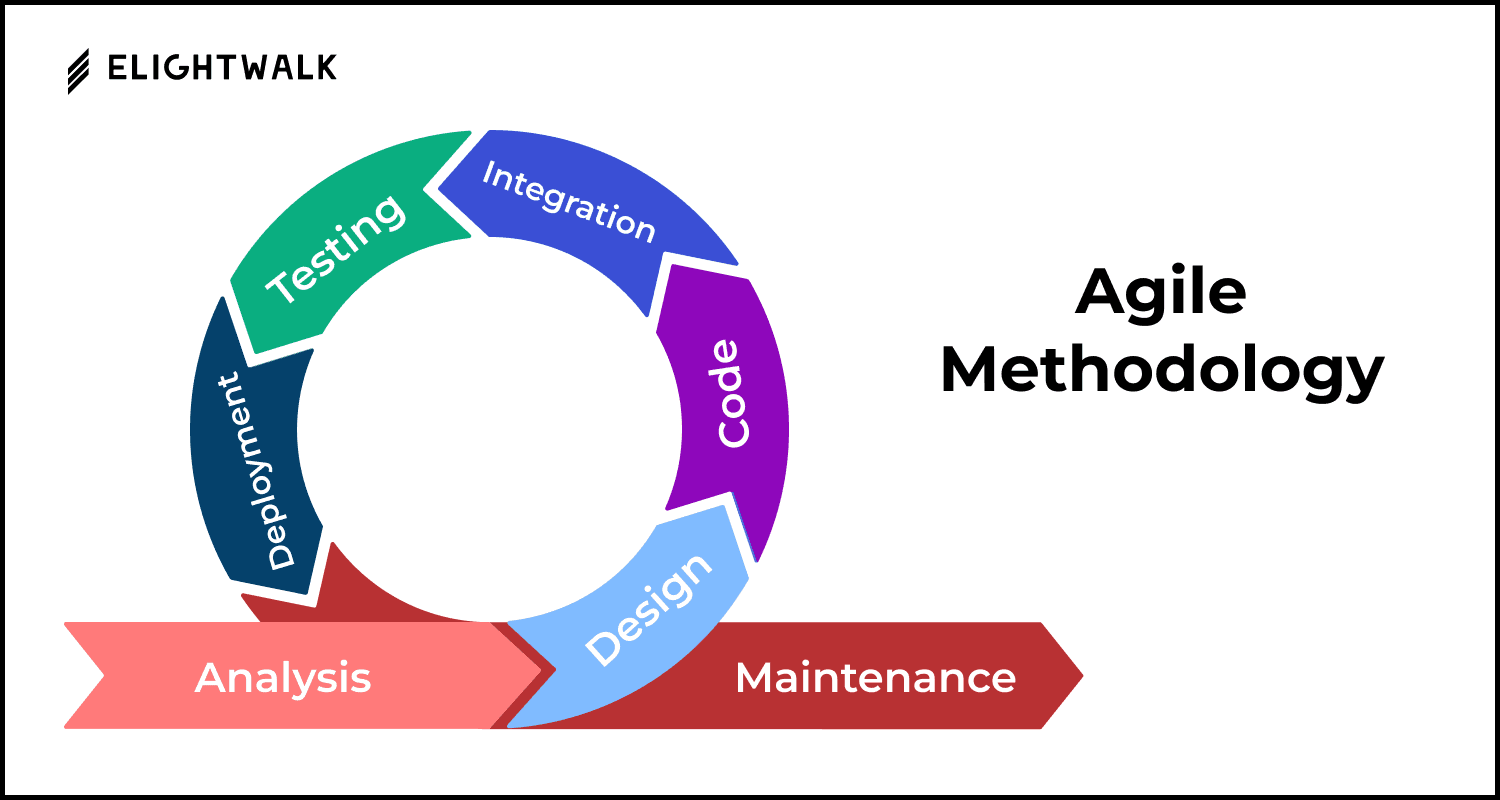
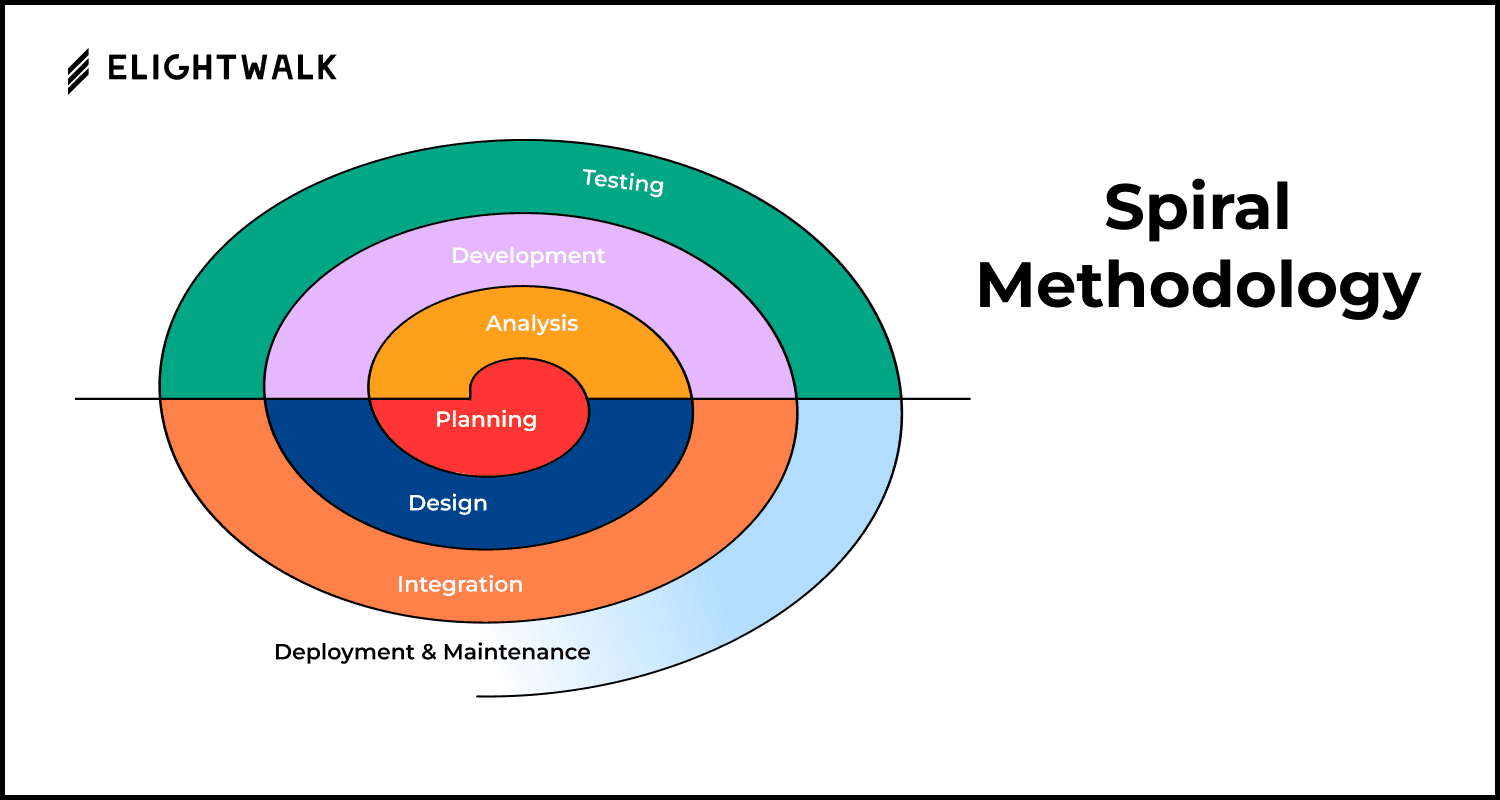
Stage 1: Planning and Feasibility Analysis
This foundational phase defines the project’s direction by assessing its purpose and practicality.
- Problem Identification: Define the issue the software aims to address.
- Goal Definition: Establish measurable objectives to guide the project.
- Stakeholder Consultation: Collaborate with clients, users, and management to gather input.
- Feasibility Study:
- Technical Feasibility: Can the system be built with available technology?
- Operational Feasibility: Will it function effectively in the desired environment?
- Economic Feasibility: Is the project financially justifiable?
Output: A high-level project plan including estimated timeline, budget, and resources.
Stage 2: Requirements Analysis
In this phase, developers and analysts gather detailed system requirements to ensure alignment with stakeholder needs.
- Requirement Gathering: Conduct interviews, surveys, and research.
- Use Case Definition: Map out system-user interactions and behavior.
- Software Requirements Specification (SRS): A detailed document that outlines technical, hardware, software, and user requirements.
Stage 3: System Design and Prototyping
This stage translates the requirements into technical specifications and early visuals.
- High-Level Design (HLD): Define architecture, data flow, and tech stack.
- Low-Level Design (LLD): Specify modules, interfaces, databases, and UI details.
- Prototyping: Create mockups or wireframes for early feedback.
Output: A Design Document Specification (DDS) used by developers during implementation.
Stage 4: Software Development
This is where actual coding begins, based on the design specifications.
- Coding: Developers write code using selected programming languages and frameworks.
- Version Control: Tools like Git are used for collaboration and tracking changes.
- Development Standards: Follow best practices and coding conventions.
- Use of Tools: IDEs, compilers, debuggers, and security scanners like SAST ensure quality.
Stage 5: Testing and Quality Assurance (QA)
Software testing ensures the product is functional, secure, and meets the original requirements.
- Unit Testing: Test individual software modules.
- Integration Testing: Ensure combined components work seamlessly.
- System Testing: Evaluate the full system in a controlled environment.
- User Acceptance Testing (UAT): Final testing by end-users.
- Regression Testing: Ensure new updates do not break existing functionality.
Stage 6: Implementation and Integration
Once testing is complete, the software is deployed in a production environment and integrated with other systems.
- System Installation: Deploy software to live servers or user machines.
- Data Migration: Transfer data from legacy systems to the new one.
- Configuration: Set up roles, permissions, and preferences.
- Pilot Testing: Soft launch to a limited group of users before full release.
Stage 7: Operations and Maintenance
After deployment, ongoing maintenance keeps the software secure, efficient, and up to date.
- Bug Fixes: Address post-launch issues and errors.
- Performance Monitoring: Track performance and identify bottlenecks.
- Feature Enhancements: Add features based on evolving business needs.
- Security Updates: Patch vulnerabilities and protect user data.
- Support & Documentation: Maintain help resources and train support teams.
The SDLC provides a clear roadmap for developing robust, scalable, and reliable software solutions, ensuring alignment with user expectations and business objectives throughout the product lifecycle.